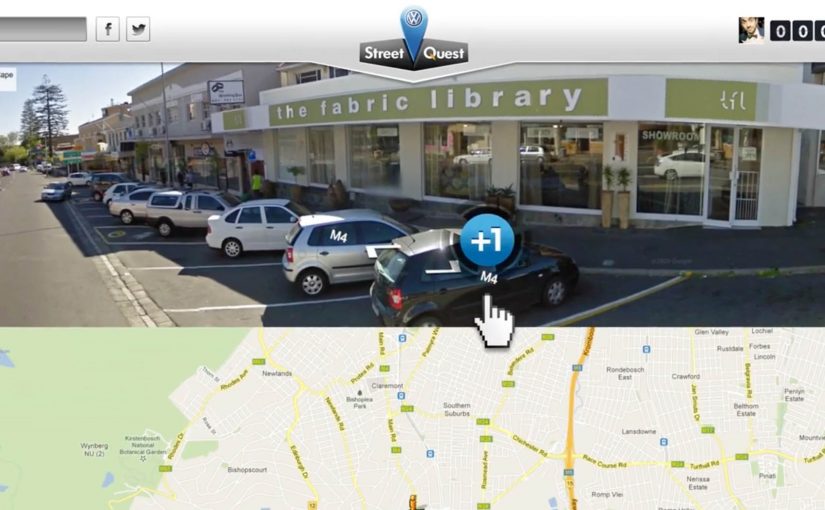
Volkswagen Netherlands set out to launch the new GTI in a way that feels fast before anyone even touches the accelerator. The result is an online race staged inside banner advertising, but mapped onto the physical logic of the real world.
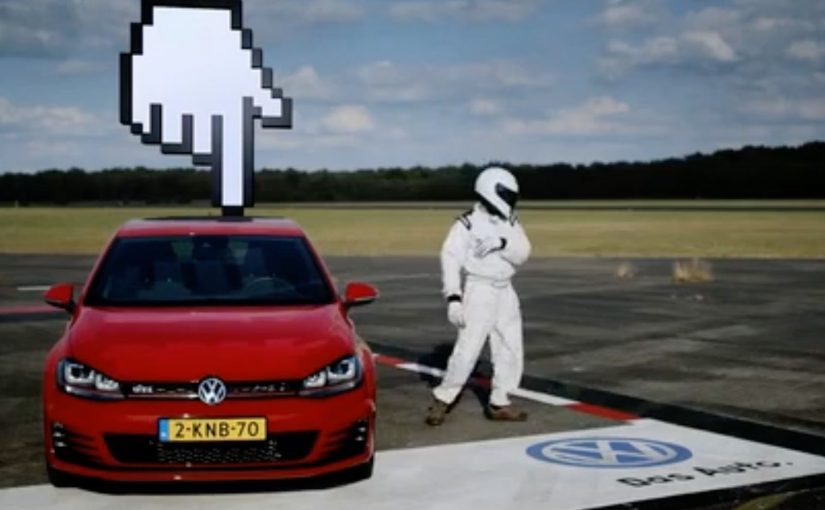
Four popular Dutch websites are painted as the runway of an airport, each banner space measuring 20 metres wide and 25 metres long. On race day, 13th September, participants chase the GTI as it speeds through the banner spaces of each site. The person fast enough to catch the new GTI wins the car in real life.
When banners stop being static and start behaving like space
The mechanism is a reframing of banner advertising. Instead of isolated rectangles, the banners become connected terrain. Each site represents a segment of runway. Movement between banners creates the illusion of distance, speed, and progression.
The GTI does not just appear. It moves. And because it moves, the user has a reason to stay alert, react quickly, and treat the banner as something to engage with rather than ignore.
In digital launch campaigns, turning passive media into an environment with rules is often the fastest way to earn attention without buying more impressions.
Why speed and scarcity do the heavy lifting
This works because it borrows from racing psychology. There is a single target. There is a clear win condition. And there is scarcity. Only one person catches the GTI. That tension transforms passive browsing into a moment of competition.
The prize is not symbolic. Winning the actual car anchors the experience in reality, which prevents the activation from feeling like a disposable digital trick.
The intent: make the GTI feel alive online
The business intent is to translate the GTI’s performance DNA into a digital format. Speed, responsiveness, and thrill are not explained. They are simulated. The banner becomes a proxy for the car’s character.
At the same time, Volkswagen demonstrates that standard media formats can still surprise when they are treated as systems instead of slots.
How it was built behind the scenes
The making-of video shows how the different banner environments were aligned, timed, and stitched together to behave like a single runway across multiple sites.
What to steal from the GTI banner race
- Rethink familiar formats. Banners can be environments, not just placements.
- Design for motion. Movement creates attention where static assets fail.
- Use a real reward. Tangible stakes raise commitment instantly.
- Connect experiences. Linking multiple sites turns reach into narrative space.
- Encode the product DNA. Let the interaction mirror what the product stands for.
A few fast answers before you act
What makes this GTI launch different from a normal banner campaign?
The banners are connected into a continuous race environment, turning advertising space into gameplay instead of static exposure.
Why use an online race to launch a car?
Because racing instantly communicates speed and performance, which are core to the GTI identity.
Does this work without the prize car?
The experience would still be novel, but the real-world reward dramatically increases urgency and participation.
What role do partner websites play?
They become part of the environment. Each site is a segment of the runway rather than just a host for an ad.
What is the main takeaway for digital launches?
When you turn media formats into systems with rules and progression, people stop skipping and start playing.