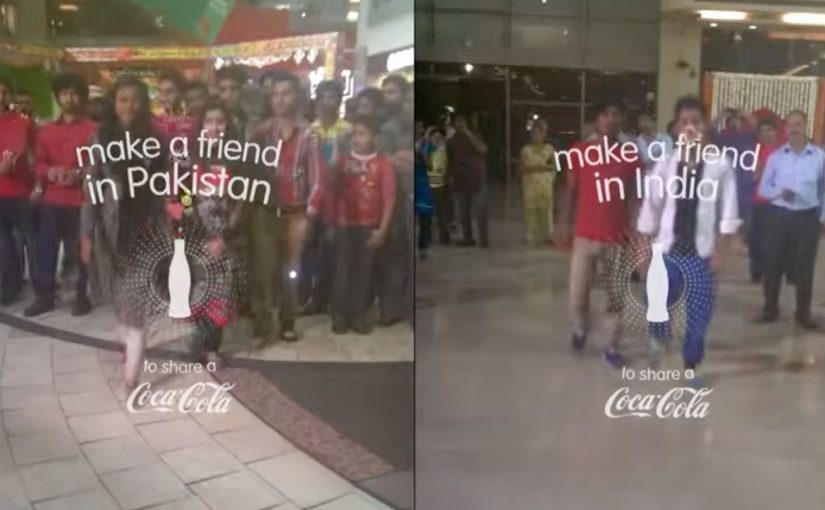Small World Machines. India and Pakistan meet through a Coke
Over the years Coca-Cola keeps experimenting with vending machines and tries to make them much more than the average soda-spitter-outer. It places two machines, one in India and the other in Pakistan, and turns them into a communication portal. These “Small World Machines” allow citizens from both countries to interact with each other and complete shared tasks. The machines reward them with a Coke. The results…
Fair Play Machines. Inter and Milan fans can only give to rivals
The success of that has inspired Coca-Cola to once again bring fighting parties together. Now instead of bringing together nations at odds, it has tapped into the rivalry between Italian soccer teams Inter and Milan.
To ease the aggression between the fans, Coca-Cola installed their “Fair Play Machines” on opposite sides of Milan’s San Siro stadium as the teams faced off. Pressing the button of one machine dropped a Coke can down the chute of that on the side of the rival team. So this way rivals could only receive Cokes from each other. The results…
What this teaches about “peace” as a design problem
The strongest move is not messaging. It is creating a constraint that makes cooperation the easiest path to a reward. When a machine encodes that rule, behaviour shifts without anyone needing to preach.
A few fast answers before you act
What are Coca-Cola “Peace Machines” in this context?
They are vending machine concepts that turn a simple Coke transaction into a social interaction, designed to reduce tension between rival groups.
What is the core mechanic of the Fair Play Machines?
Pressing the button on one machine sends a Coke to the machine on the rival side. Rivals can only receive Cokes from each other.
How do Small World Machines relate to this?
They use the same principle. A machine becomes a bridge, enabling people in opposing contexts to interact and complete shared tasks that lead to a reward.
What is the main design lesson for brands?
If you want behaviour change, build the rule into the experience. Make the cooperative action the trigger for the reward, and keep it simple enough to understand instantly.