When choice made the Elantra harder to buy
In North American automotive marketing in 2012, the hardest moments are often the ones created by success: when a winner expands and the buyer suddenly has more to compare.
The Hyundai Elantra was named 2012 North America Car of the Year. Momentum was strong.
Then Hyundai introduced two additional variants. The Elantra Coupe and the Elantra GT. Suddenly, a clear win turned into a harder purchase decision.
More choice created more hesitation. Hyundai needed to simplify the decision again, without reducing the range.
Turning your driveway into the showroom
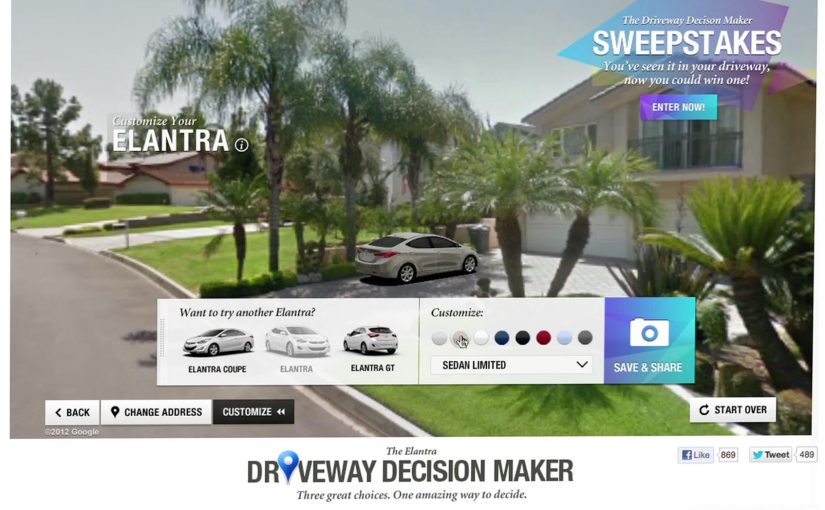
Instead of pushing another brochure or comparison chart, Hyundai built the Driveway Decision Maker.
By combining Google Street View, projection mapping, and real-time 3D animation, prospective buyers could see exactly what an Elantra would look like parked in their own driveway.
The experience replaced imagination with visualization. No guessing scale. No abstract renders. Just your house, your street, and the car.
Why seeing it at home removed friction
Car buying is emotional, but doubt creeps in when people cannot picture ownership.
The Driveway Decision Maker collapsed distance between consideration and ownership. By anchoring the car to a familiar, personal environment, Hyundai removed uncertainty about fit, size, and presence.
The experience also shifted control to the viewer. Instead of being told what to like, buyers explored the car in their own context.
The business goal behind the experience
The intent was not novelty.
Hyundai wanted to reduce decision paralysis created by a broader lineup and move people confidently from interest to purchase. By helping buyers visualize the outcome, the brand shortened the path to commitment.
This was about restoring clarity, not adding noise.
What brands can steal from Driveway Decision Maker
- Bring the product into the customer’s world. Context beats abstraction.
- Replace imagination with visualization. Show the outcome, not the promise.
- Use technology to remove doubt. Innovation works best when it answers a real buying question.
- Support choice instead of limiting it. Help people decide rather than forcing simplification.
Hyundai invited consumers to try the experience themselves at www.pickmyelantra.com.
A few fast answers before you act
What problem was Hyundai solving?
Too much choice created hesitation. Buyers struggled to decide between Elantra variants.
How did the Driveway Decision Maker work?
It combined Google Street View, projection mapping, and real-time 3D animation to place the car into a buyer’s actual driveway.
Why was this more effective than a configurator?
Because it grounded the decision in a personal, familiar environment instead of abstract specifications.
What business outcome did Hyundai target?
Reducing purchase friction and restoring confidence across an expanded model lineup.
What is the transferable lesson?
If your product requires imagination to buy, use technology to make the outcome visible.